Changes of state of matter
- Fusion (from solid to liquid)
- Solidification (from liquid to solid)
- Evaporation (from liquid to gas)
- Condensation (from gas to liquid)
- Sublimation (from solid to gas)
The plases of matter have the same properties. When the change of state happens the temperature of the substance does not change (as the ice melts, the temperature does not change during its process). Let us examine the various changes in detail.
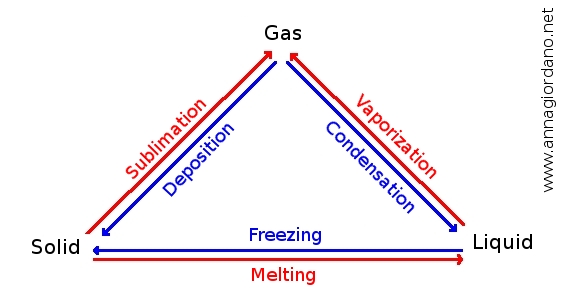
Changes of phases of matter
Melting
Melting is the transition from the solid state to the liquid one, it occurs when the heat is absorbed by the substance which changes state (matter begins to melt at a Tf temperature. While melting happens the temperature remains constant. In the T2 - T1 interval solid and liquid state coexist . The amount of heat needed to melt a mass m of a substance at the melting temperature depends on the type of substance and it is directly proportional to the mass. Heat (J) = Q = λ f m. The latent heat of fusion is the amount of heat to be supplied to 1 kg of the substance which is above the melting point, so that it can be completely melted. In the International System, the latent heat of fusion is measured in joules per kilogram.
Solidification
Solidification is the inverse of melting , a liquid solidifies when it becomes solid. The transition occurs at the same temperature at which melting occurs, for example, water solidifies at 0 ° C. Solidification of a liquid takes place by emission of heat. The latent heat of solidification is the heat that the unit mass of liquid provides during the passage of state and it is numerically equal to the latent heat of fusion. Example: to melt 1 kg of ice at 0 °C 334 000 J are needed; when 1 kg of water at 0 °C solidifies and becomes ice, it produces 334000 J of heat. The temperature of the liquid goes down and it begins to solidify at the Tf- temperature. While it solidifies the temperature remains constant. During T1-T2 interval liquid and solid coexist.
The evaporation and condensation
Evaporation or vaporization is the passage from liquid to gas and it happens thanks to absorption of heat by the liquid that changes state. During evaporation the temperature remains constant. The latent heat of vaporization is the amount of heat absorbed by a unit mass of liquid, which is already at the temperature of evaporation and finally moving to the gaseous state. The heat in order to evaporate a substance of mass m of matter that is at the boiling point, is directly proportional to the mass.
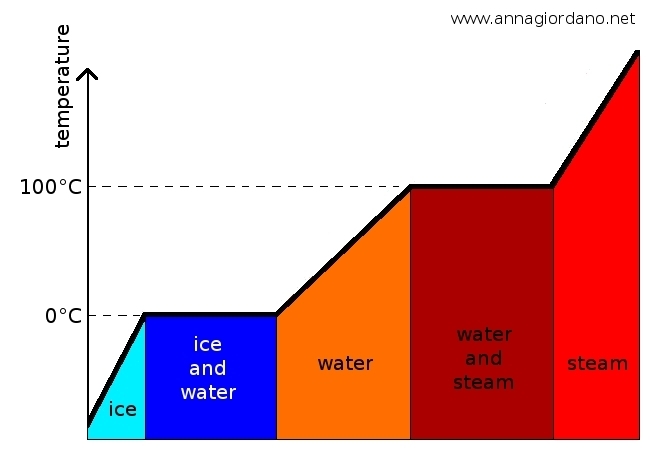
Changes of phases of water
In Italian
|